Osmanli Devleti
INEGOL ITS EARLY OTTOMAN CONQUEROR
Inegöl & its early Ottoman conqueror, Turgut Bey
(Translated from the official Inegöl City & Inegöl Chamber Of Commerce & Industry webpages & also some available translations of early chronicles)
If you want, you can skip sections on ancient history of İnegöl & go straight to early Ottoman history [that is being showcased ın Kuruluş Osman Season 3]
About the Name of İnegöl
The name of İnegöl in the Byzantine Period was Angelacoma. However, a source has not yet been found to confirm the claims that the name İnegöl is the distorted pronunciation of Angelacoma.
In the sources, it is seen that the name İnegöl was written in different forms. However, it is known that in most of the Ottoman sources it was written as Ayna-Göl or İne-Göl.
Evliya Çelebi, tells in his travel book that İnegöl is derived from Ezinegöl; He narrates that İnegöl took the name “Ezinegöl” because it was conquered on Friday, that is, Ezine day according to the parlance of those days, and that in time, the “Ez” part at the beginning was removed and it was called only İnegöl.
Archeological Surveys.
The history of İnegöl, according to the findings of the archeological surveys carried out in 1847 and 1942, dates back to 3000 BC. There are 6 mounds of archeological interest in İnegöl, namely Cumatepe, İnegöl 2, Şıbalı, Boğazköy, Palangatepe and Kurşunlu.
Today, the mound in the middle of the city, around the municipality headquarters, is called Cumatepe.
During excavations carried out by Bursa Archeology Museum in 1999 on the Cumatepe mound in the city center, mixed aged objects ranging from the Late Ottoman to the Chalcolithic Period were found.
Inegol in Antiquity
İnegöl has been invaded frequently due to its strategic location on military and commercial routes since ancient times.
It has been determined that Phrygians, Lydians, Persians and Macedonians successively ruled in İnegöl, which has a history of 5000 years. In 74 AD, it came under the rule of the Roman Empire.
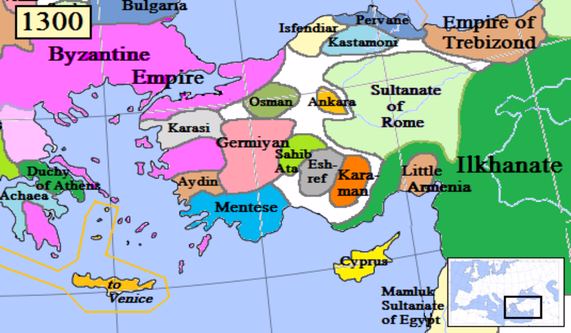
And after the split of the Roman Empire in 395 AD, İnegöl passed under the rule of the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine). It continued to be under Byzantine rule as a Tekfurluk center until the establishment of the Ottoman Principality by Osman Ghazi.
The Establishment of the Ottoman State and the Conquest of İnegöl
Osman Bey, who became the head of the principality in 1281 upon the death of his father Ertuğrul Bey, began the conquests against Byzantium soon after.
[Official Webpage from Inegol Chamber Of Commerce & Industry also adds that Osman Bey initially followed a policy of maintaining cordial, good working, relationships with the feudal landlords in Bursa, Bilecik and surroundings. Except with Ayah Nikola.]
In a battle with Ayah Nikola, the battle of Ermeni Beli in 1284, he and his men had to retreat after the martyrdom of Baykoca, the son of his brother, Savcı Bey.
Baykoca was the first martyr of the dynasty and his grave is in Hamzabey District of İnegöl.
Despite the retreat (and Bayhoca’s martyrdom), Ottoman history began with this first military operation.
The foundations of a state that would rule for six centuries were laid in the quadrangle of Söğüt, Bilecik, Domaniç and İnegöl in a short period of time.
After a while, Osman Bey raided Kulaca Castle near İnegöl and conquered the castle. The year of this conquest event was recorded as Hijri, 684, Gregorian, 1285 in the chronıcles of Aşıkpaşazade, and it was stated that this conquest was the first conquest of Osman Gazi.
[It is also mentioned in some early chronicles that deeply affected by Bayhoca’s martyrdom, Osman Bey never visited Angelacoma (İnegöl) and surroundings for approximately 14-15 years, while continuing with conquering other castles – the Karcahisar (İnönü Castle), Bilecik and Yarhisar Castles. A great many friends of feudal landlord of Angelacoma were thus erased from history]
Concerned about these developments, İnegöl tekfuru, Nikola, formed an alliance with other tekfurs to eliminate Osman Bey.
Osman Bey, becoming aware of this alliance, assigned the conquest of İnegöl to his comrade, Turgut Alp.
[in many early sources, Turgut Alp is referred to as Osman Bey’s dear friend & comrade – which make it reasonable to assume that age wise, he ‘might’ have been Osman Bey’s contemporary. This is the more widespread understanding & the reason why in the earlier TRT series on Osman Bey, he was shown as Osman Bey’s contemporary & friend]
With the siege plan implemented by Turgut Alp, İnegöl was finally conquered in 1299. After this conquest, Osman Bey handed over the administration of İnegöl and its surrounding villages to Turgut Alp.
[[According to early Ottoman sources, Turgut Alp was also with Osman Bey during the conquest of ‘Yarhisar’ and was then commissioned with the conquest of Inegol. In these sources, it is also mentioned that Turgut Alp first sieged the city and then Osman Bey came to his aid. It was also mentioned that during the conquest of Inegol, the city’s Tekfur, Aya Nikola, was executed and thereafter, Osman Bey assigned the administration of Inegöl & ıts surrounding villages to Turgut Alp]
The region where Inegol’s Kirles (Paşaören), Süle, Genci (Turgutalp Village), Gelene (Kayapınar) and Kıran Neighborhoods are located were called the Turguteli-Turgutlar district.
Turgut Alp, who also contributed significantly in the subsequent conquest of Bursa by Sultan Orhan, passed away in the village of Genci (today’s name Turgut alp Köy Mahallesi), where he had settled in his later years.
His mausoleum is on a large hill overlooking İnegöl in Turgut Alpköy Mahallesi, and a memorial ceremony is held around the mausoleum every year on the day of Hıdrellez.
The naming of a neighborhood, a village, an Anatolian High School and a mosque in İnegöl after Turgut Alp is an indication of the place this highly successful early Ottoman commander holds in the collective memory of generations that came after him.
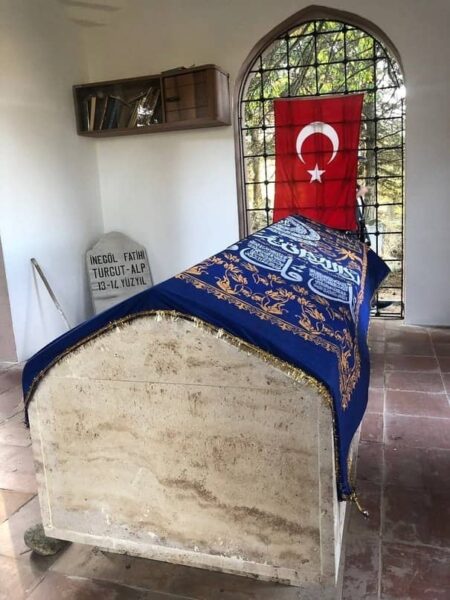

Turguts Burial Place
Osmanli Devleti
The Clock Towers From The Archive Of Sultan Abdul Hamid
The Clock Towers From The Archive Of Sultan Abdul Hamid
The clock, which provided great convenience to people with its invention, was located in the city squares at a size and height that everyone could see before it got smaller and went into pockets. Although they were built in the West, these historical buildings, which became works of art in the East, were the most striking architectural works of the cities. On the 25th anniversary of Sultan AbdulHamid’s accession to the throne, it spread to the interior of Anatolia, with the governors sending an edict to build a clock tower. We have compiled the photographs of clock towers that have witnessed centuries from the archive of Sultan AbdulHamid.

Amasya Clock Tower

Ankara Clock Tower

Baghdad Clock Tower

Balıkesir Clock Tower

Balıkesir Clock Tower

Darülfünun building and clock tower in Mumbai, India
Architectural works of the period reflect this feature because they were built in baroque, empire, eclectic and neo-classical styles. Clock towers are usually plain stone structures. Clock towers in Tophane, Yıldız Palace, Dolmabahçe, İzmir and İzmit are the most ornate.

Clock tower in the garden of Osman Gazi tomb
The clock tower located in Tophane Park in Bursa; It was first built during the reign of Sultan Abdulaziz. It was demolished at an unknown date, however, until the 1900s. Its construction started again in 1904 and was completed on August 31, 1905. It was put into service with a ceremony by the Governor Reşit Mümtaz Pasha on 31 August 1906 in honor of Abdülhamid’s accession to the throne.

Edirne Clock Tower
The tower, which became known as the “Macedonian Clock Tower” after the wooden floors and clocks that had been built by Hacı İzzet Pasha, one of the governors of Edirne, on the tower in 1866-1867, was severely damaged in the 1953 earthquake.


Gümülcine Clock Tower

Halep Clock Tower

İzmir Station Clock Tower

Konya Clock Tower

Samarra Cami (Mosque) Clock Tower

Samsun Clock Tower

Tophane Clock Tower

Tripoli Clock Tower

Yanya Clock Tower

Yıldız Palace Hamidiye Clock Tower
Hamidiye Clock Tower is located in Yıldız district of Beşiktaş district of Istanbul. As it can be understood from the tugra on the entrance gate, it was built by AbdulHamid II between 1889 and 1890. The architect of the clock tower, which was built with four sides (octagon) with broken corners, is Sarkis Balyan. There are four inscriptions on the first floor of the tower, a thermometer and barometer on the second floor, and a clock room on the top floor. There is a compass on the decorative roof of the clock tower and a weather vane on its top.

Yozgat Clock Tower
Osmanli Devleti
COUNTRIES RULED FOR YEARS BY THE OTTOMAN
COUNTRIES RULED FOR YEARS BY THE OTTOMAN!
1. Turkiye (…)
2. Bulgaria (545 years)
3. Greece (400 years)
4. Serbia (539 years)
5. Montenegro (539 years)
6. Bosnia and Herzegovina (539 years)
7. Croatia (539 years)
8. Macedonia (539 years)
9. Slovenia (250 years)
10. Romania (490 years)
11. Slovakia (20 years) Ottoman name: Uyvar
12. Hungary (160 years)
13. Moldova (490 years)
14. Ukraine (308 years)
15. Azerbaijan (25 years)
16. Georgia (400 years)
17. Armenia (20 years)
18. Southern Cyprus (293 years)
19. Northern Cyprus (293 years)
20. Southern lands of Russia (291 years)
21. Poland (25 years)-protection- Ottoman name: Lehistan
22. The southeast coast of Italy (20 years)
23. Albania (435 years)
24. Belarus (25 years) -protection-
25. Lithuania (25 years) -protection-
26. Latvia (25 years) -protection-
27. Kosovo (539 years)
28. Vojvodina (166 years) Ottoman name: Banat
29. Iraq (402 years)
30. Syria (402 years)
31. Israel (402 years)
32. Palestine (402 years)
33. Urdun (402 years)
34. Arabia (399 years)
35. Yemen (401 years)
36. Oman (400 years)
37. United Arab Emirates (400 years)
38. Qatar (400 years)
39. Bahrain (400 years)
40. Kuwait (381 years)
41. Western lands of Iran (30 years)
42. Lebanon (402 years)
43. Egypt (397 years)
44. Libya (394 years) Ottoman name: Tripoli
45. Tunisia (308 years )
46. Algeria (313 years)
47. Sudan (397 years) Ottoman name: Nubia
48. Eritrea (350 years) Ottoman name: Habes
49. Djibouti (350 years)
50. Somalia (350 years) Ottoman name: Zeyla
51. Kenyan beaches (350 years)
52. Tanzanian beaches (250 years)
53. Northern regions of Chad (313 years) Ottoman name: Reşade
54. Part of Niger (300 years) Ottoman name: Kavar
55. The northern lands of Mozambique (150 years)
56. Morocco (50 years) -protection-
57. Western Sahara (50 years) -protection-
58. Mauritania (50 years) -patronage-
59. Mali (300 years) Ottoman name: Gat Kazası
60. Senegal (300 years)
61. Gambia (300 years)
62. Guinea-Bissau (300 years)
63. Guinea (300 years )
64. Part of Ethiopia (350 years) Ottoman name: Habeş (Abyssinian)
Although not officially located within the borders of the Ottoman Land borders, the places that are actually connected to the Caliphate are:
65. Muslims of India -Pakistan-
66. East India Muslims -Bangladesh-
67. Singapore
68. Malaysia
69. Indonesia
70. Turkestan Khanates
71. Nigeria
HISTORY
ORHAN GAZI AND HIS RELATION WITH EUROPE
The year is 1326 and Osman Gazi has died from natural causes during the siege of Bursa shortly after Osman’s that the city of Bursa was taken by his oldest son Orhan Ghazi. Orhan Ghazi and his stepbrother Aladeen Pasha would talk about the line of succession to the Beylic that they both inherited. The Step Brothers came to conclusion that Ottoman Beylic shouldn’t be split between them Aladeen relines that Orhan was natural born warrior whereas he was more of a man of learning and education didn’t fit the mould of a military commander. He wanted to continue to administrate the Beylic while his more charismatic brother Orhan went on military campaigns so Orhan Gazi became the new Sultan rewarding his stepbrother’s loyalty to him and to the state he made a Aledeen Pasha the first Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire, an office which would be occupied by various men until 1922.
Orhan Ghazi would start his dream by moving the Ottoman capital to Bursa rewarding the Byzantine commander for surrendering the city to him by giving him and his sons key positions in the ottoman army to serve him. This was a common practice also seen when Osman Gazi gave the former Byzantine governor Kosemihal major positions in the Ottoman administration after he surrendered his City to Osman Gazi. The new capital Bursa was transformed by many building projects paid by Aladeen Pasha which saw many mercantile establishments bazaars open in the city which turned the city into a major trade centre in the region.The transformation of Bursa indicates a turning point for Ottoman Turks which sees them go from the nomadic hurts people into a settled urban society.
By the year 1328 the Byzantine civil war concluded with the overthrowing of Emperor Andronikos II along with the serbian allies by his grandson Andronikos III who was backed up by the Bulgarians. Also by that time Orhan had started the siege of Nicaea was the second biggest city in the Byzantine Empire only second to their capital of Constantinople. Andronikos III decided to relieve the important besieged city of Nicaea and hope to restore the Byzantine frontier to a stable position. Andronikos III led an army of about four thousand men which was greatest he could muster at the time to the besieged city. An 8,000 strong Ottoman army led by Orhan Ghazi would strike this Byzantine force floors during the Battle of Pelekanon. The battle would be a Ottoman victory which would see Andronikos III being wounded during battle, this would be the last time the Byzantine’s would attempt to try to regain land in Anatolia the huge city of Nicaea would fall to the ottomans by 1331 and in 1333 Orhan and his son Suleyman Pasha would start the siege in Nicomedia which would fall in 1337.
While Orhan Gazi and his armies where military campaigning against the Byzantines Aladeen Pasha was administrating the Empire at the capital of Bursa. He introduced the monetary system into the state which would see the first coining of ottoman coins under the name of Orhan. Aladeen would also reorganized the Ottoman army into a standing army. Aledeen Pasha formed the new army by forming cores the paid infantry which was to be kept in constant readiness for military service these troops were called the Yaya infantry. This army was highly organized unlike their previous Ghazi Army’s. Aladeen Pasha’s clothing reforms were also very important to the multi-ethnic Beylic, different attires were chosen for different ethnicities which made it easier to identify people’s backgrounds. The Ottoman Beylic was a diverse state which saw many Greeks Turks Armenians and Jews live together. This reform was not to single a community but to give ethnic groups identity in which the state could easily interact with those people. The people that lived under the Ottoman Beylic had a close relationship to their central government unlike many feudal kingdoms.
Aladeen Pasha’s reforms ensured the legitimacy of the new Ottoman government on the lands inwhich that ruled and that would survive from outside threats while at the same time making it easier to conquer more land and interact with the conquered people.
Aladeen Pasha the first Grand Vizier of the Ottoman state will pass away in Bursa in 1331 leaving behind stable government for his warrior stepbrother Orhan Ghazi to manage.
By 1345 the Karasids Beylic to the west was in turmoil Yashi Han the leader of the Karasa Balak had died and his two sons would start a civil war in order to become the next Bey. Orhan Gazi saw an opportunity to gain further power in the region by participating in civil war, this pretext for war was that he was trying to establish peace in the Karasids Beylic. By the end of the year one of the brothers in a rebellion were killed in battle and the other one was captured by Orhan Gazi. The rich Beylic of Karasids and its huge Navy was taken over by the Ottoman Beylic. The Ottomans were eyeing the shores of Europe across the Dardanelles straits planning their next move.
After the battle Pelican in 1329 the ottomans and the Byzantines entered a period of threatening contact due to both sides not wanting to continue their three-decade war with each other.
The Byzantine state was crumbling at a very fast rate and they were also defeated by the Bulgarians to the Battle of Rooster Castro and 1332 which almost kicked out the Byzantines from the region of Thrace. Things went worse in 1341 when Andronikos iii died this would start another round of civil wars for the Byzantines. Andronikos son John V was only nine years old when his father died, so Andronikos Chief Minister John VI vied for power left by the power vacuum after the death of Andronikos and became the new emperor. John VI would win the Civil War and become the senior Emperor in Regent for ten years for the junior emperor John v until he was old enough to rule by himself Serbian and Bulgaria took big chunks of land from Byzantines during the Civil War. The Byzantines desperately needed a new ally to protect them from Serbia and Bulgaria so John the IV turned to Orhan Ghazi for help.
John VI would ally himself with Orhan Gazi by planning a royal marriage between his daughter Theodora and Orhan to declare their friendship to one another. In 1346 Orhan Gazi would marry Theodora in Constantinople in the following year the couple would have a sudden name Shahzade Halil. This alliance however failed to prevent the Byzantines from further decline, this was evident during the Byzantine Genoese war of 1348 to 1349 where the Byzantines failed to prevent Genoa from occupying the Golden Horn right next to Constantinople due to tariff disputes. To show off their presence in Constantinople the Genoese built the Galata Tower which became the tallest building in the city. The ottomans wouldn’t join this war with the Byzantines due to the Byzantines allying themselves with Venice. The Venetians and the Ottomans were hostile to one another due to Orhan’s raiding parties against relationships and Dardanelles this meant that Orhan would not participate during this war. After years of unrest and John VI losing his popularity with the people and the government the Byzantines were yet again in a civil war. In 352 John the V he was twenty years old by this time had revolted against John VI to become the sole ruler of the Empire which he inherited from his father. Seeing a way to gain further influence with the young Emperor and gain even more land Serbia Genoa and even Venice sided with John the fifth.
Hearing about John the V’s revolt against him John the VI made his son Matthew Emperor and requested help from Orhan Gazi. Orhan Gazi also seen an opportunity to gain land in Europe decided to help his father-in-law John VI and sent over ten thousand of his best warriors over the Bosporus to stop John V revolt. The battle of DemoTika saw the joint forces of Orhan Ghazi and John VI wipe out the forces of John V and his Serbian allies, this battle would be the first battled the Ottomans would fight on European soil and resulted in a victory for Orhan Ghazi. It was at this point Orhan Gazi was becoming a popular figure among Turkish Beylics back in Anatolia.
Hearing about John the V’s revolt against him John the VI made his son Matthew Emperor and requested help from Orhan Gazi. Orhan Gazi also seen an opportunity to gain land in Europe decided to help his father-in-law John VI and sent over ten thousand of his best warriors over the Bosporus to stop John V revolt. The battle of DemoTika saw the joint forces of Orhan Ghazi and John VI wipe out the forces of John V and his Serbian allies, this battle would be the first battled the Ottomans would fight on European soil and resulted in a victory for Orhan Ghazi. It was at this point Orhan Gazi was becoming a popular figure among Turkish Beylics back in Anatolia.